Twelve-year-old Jonas lives in a seemingly ideal world. Not until he is given his life assignment as the Receiver does he begin to understand the dark secrets behind this fragile community.
The Giver by Lois Lowry, 2006
Twelve-year-old Jonas lives in a seemingly ideal world. Not until he is given his life assignment as the Receiver does he begin to understand the dark secrets behind this fragile community.
The Giver by Lois Lowry, 2006
我记录了ddrescue成功对未识别移动硬盘进行数据抢救。朋友圈里朋友索要可执行文件。我整理了一下,供大家参考。请大家一定check .zip文件的md5 sum,确保不是来自于其他给加了乱七八糟来源的文件。
–使用说明:
ddrescue 1.24 executables for win
1 解压缩至某文件夹,如 d:\ddrescue-1.24-cygwin
2 将旧盘与新盘均插入机器上;
3 打开命令行窗口,即 win+r,敲入 cmd;
4 切换当前目录到步骤1所在的文件夹,即在命令行窗口敲入: cd d:\ddrescue-1.24-cygwin。文件夹名根据步骤1确定。
5 命令行里敲入 cat /proc/partitions,结果应该如下所示:
major minor #blocks win-mounts
8 0 xxx sda
8 1 xxx sda1 C:\
8 2 xxx sdb
8 3 xxx sdb1 D:\…
根据最末列的win盘符确定旧盘和新盘的设备名(如/dev/sdb2即是对应于D盘)。
Continue reading症状:Win 10下西数4TB 移动硬盘不能识别,explorer里显示盘符,但无法打开,explorer界面无响应,拔出再次插入,提示该盘不对,问是否格式化(千万不要点格式化)。
心情:平时都能及时备份,最近一偷懒就出现情况,傻眼了。
材料:不能识别的老盘;一块新的4TB 西数Elements 移动硬盘;ddrescue
Continue reading被誉为世界“第三极”的青藏高原是全球中低纬度地区海拔最高、面积最大的多年冻土区,被称为全球变化的“驱动机”和“放大器”。过去50年青藏高原变暖趋势明显,导致多年冻土发生显著退化,进而严重影响到区域水文、生态乃至全球气候系统。近30年高原变暖速率显著增加,且冬季变暖速率快于夏季变暖。这就引发了一个重要的科学问题,即冬季变暖如何影响整个高原多年冻土的变化。然而,迄今为止,尚未有研究评估多年冻土对冬季变暖的响应。
针对上述科学问题,我们以数值实验为手段,首次研究了青藏高原冬季变暖对多年冻土的影响,结果表明:
该研究通过假设数值实验首次研究了冬季变暖对多年冻土变化的影响,为理解青藏高原多年冻土对季节性变暖的响应提供了一个新的视角。
Continue reading今天更新了一下win10的新版本1903 (2019年5月份的比较重大的版本),结果出现问题了:
windows search 不能用了
任务管理器里可以看到,Cortana (小娜)占用的CPU 很高,40-50%模样。
搜索了Google,有各种方案,比如通过组策略(gedit)或者注册表来禁用Cortana 等,但好像都不好用。问题是由于1903版本带进来的没有问题,所以缩小关键词后进一步搜索,发现微软已经在前些天(9月初)对应已经发布新的更新。在Windows Update 里搜索新更新,会发现有新的可用更新,安装后,结果又出现问题,具体表现是Search 仍然不能用,而且 Search 线程使用CPU 居高不下。
现次搜索,原因大概是微软解决了老问题,又引入了新问题。是由于一个 KB4512941 更新导致的。这个帖子里有讨论,而且给了一些可能的方案。我发现将这个更新卸载掉,重启机器,前面出现的search 不能用,CPU 占用过高等问题已经解决。具体步骤大概是: Continue reading
摘要:“ GIS 算法基础”课程是高校GIS 专业主干课该课程具有理论性强、内容碎片化、前沿性和知识面广的特点,对数学和计算机的能力要求高,学生学习和教师授课都有较大难度。文章总结了南京师范大学GIS 专业开展该课程的教学经验提出注重基础、兼顾前沿、旨在启迪的原则和问题求解导向、整体把握、翻转课堂、同伴教学等针对性措施此外还应通过大量实验课程来巩固教学效果和驱动学生主动学习。
南卓铜,张宏,潘雪莹,高红侠,赵淑萍. “GIS算法基础”课程教学研究. 高等理科教育. 2019(3): 114-120.
Zhao Y, Nan Z*, Yu W, Zhang L. Calibrating a hydrological model by stratifying frozen ground types and seasons in a cold alpine basin. Water. 2019, 11(5): 985. DOI:10.3390/w11050985.
Abstract: Frozen ground and precipitation seasonality may strongly affect hydrological processes in a cold alpine basin, but the calibration of a hydrological model rarely considers their impacts on model parameters, likely leading to considerable simulation biases. In this study, we conducted a case study in a typical alpine catchment, the Babao River basin, in Northwest China, using the distributed hydrology–soil–vegetation model (DHSVM), to investigate the impacts of frozen ground type and precipitation seasonality on model parameters. The sensitivity analysis identified seven sensitive parameters in the DHSVM, amid which soil model parameters are found sensitive to the frozen ground type and land cover/vegetation parameters sensitive to dry and wet seasons. A stratified calibration approach that considers the impacts on model parameters of frozen soil types and seasons was then proposed and implemented by the particle swarm optimization method. The results show that the proposed calibration approach can obviously improve simulation accuracy in modeling streamflow in the study basin. The seasonally stratified calibration has an advantage in controlling evapotranspiration and surface flow in rainy periods, while the spatially stratified calibration considering frozen soil type enhances the simulation of base flow. In a typical cold alpine area without sufficient measured parametric values, this approach can outperform conventional calibration approaches in providing more robust parameter values. The underestimation in the April streamflow also highlights the importance of improved physics in a hydrological model, without which the model calibration cannot fully compensate the gap.
Keywords: parameter calibration; cold alpine basin; frozen ground; precipitation seasonality; sensitivity analysis; distributed hydrology–soil–vegetation model
官方下载链接:Link
在办公室时,我Laptop往往连着一个外接大屏幕工作,离开时就直接把线一拔。一些应用程序像NoteExpress,进入扩展屏幕模式后在扩展屏幕上使用,当拔下扩展屏幕连接线,NE界面仍然还在扩展屏幕上(有些程序能自动回来主屏幕,明显NE在这方面考虑的很不够),在当前屏幕上就看不到,以后打开NE,也都是恢复到此前位置(即不存在的扩展屏幕上)。
通过以下方法解决:
用Alt + Tab 切换到NE为当前窗口(激活状态) ,用快捷键 Alt + (空格键) 激活菜单,再按 M (移动) ,就可以通过左右方向键移窗口至可视区域。
如果Alt+空格被别的程序所占,如Find and Run Robot,那么在进行上述操作前,关闭之。
其它多数应用程序也都按如上方法恢复。如果实在不行,那么就找一块外接屏幕,接上,然后将外接屏幕的程序拉回当前屏幕,然后再拔掉。
南卓铜 ([email protected])
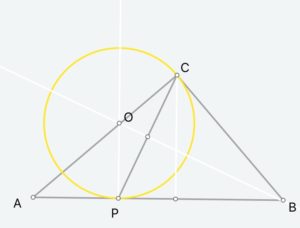
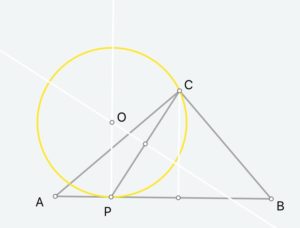
我之前介绍过这个ios上的小app,功能很强大。微信有朋友反映说用起来还是有点困难。的确是这样。昨天又碰到小朋友问一个动点问题,他们老师讲的她理解不透。
这个问题是:
【2014玄武一模】在△ABC中,∠ACB=90°,经过点C的⊙O与斜边AB相切于点P.