下图是某初中课本上阐述水资源时间分配不均的配图。Z老师在微信上问我单位有没有问题。后来也得知不少中学老师也发现了不对。这里单位的确错了。但其实这里涉及的概念还是挺多挺乱的,需要好好讲讲。
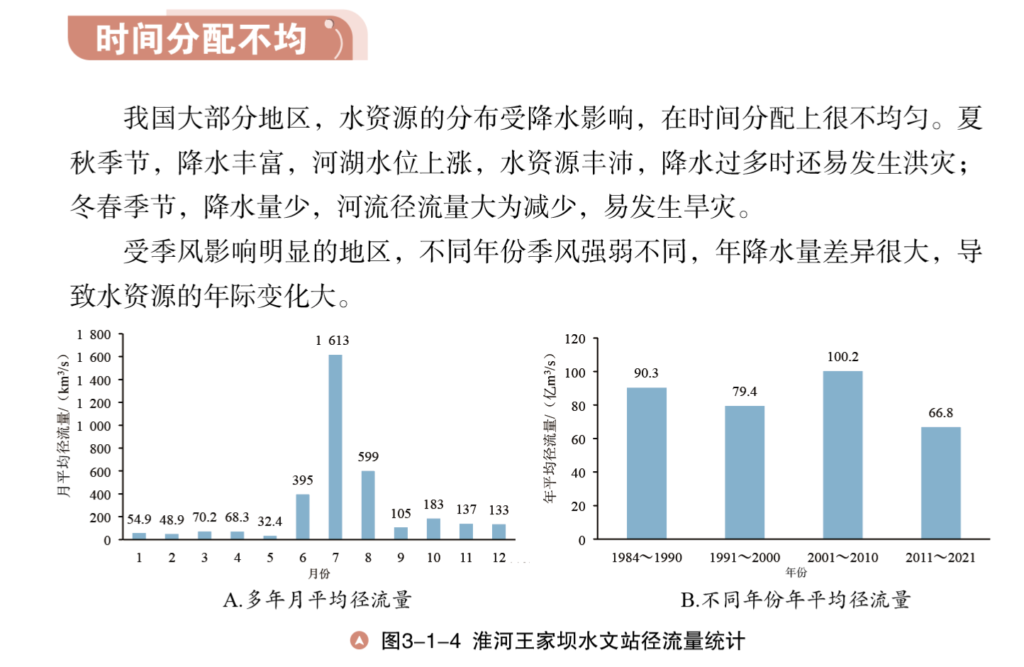
下图是某初中课本上阐述水资源时间分配不均的配图。Z老师在微信上问我单位有没有问题。后来也得知不少中学老师也发现了不对。这里单位的确错了。但其实这里涉及的概念还是挺多挺乱的,需要好好讲讲。

1 水文是大类课程,260余人分6个班级组合为3个大班教学,考试结果第1名的同学是文科生(劳动与社会保障)转来地理并降级的。我跟学生讲,学生说“啊是嘛 (可能因为题型比较固定所以我有重点复习叭” (sic.),然后说“可能是我复习的还挺认真的缘故? hh” (sic.) 。讲的是一点都没有信心。于是我检查了一下作业和试卷,都完成的很漂亮。因为每次作业(共12次)和试卷里的每道题都由一个老师统一批改全部学生,这个综合成绩是很真正反映水平的。只是这么多理科生让文科生拿了第一,这面子何在,哈哈。
2 4班一对学生A与B,A疑问“我想了一个晚上,还是不知道为什么我的期末考的这么低……舍友(B)她说她计算题好几个不会,期末都考了86”,B也说老师她感觉成绩有点高了。于是我们仔细核查了作业和试卷,A的试卷考的很不理想,远低于B,因为作业分还拉上来不少。而B试卷考了高分,作业以及问问题都很有深度,取得高分也实属正常,而所谓的计算题不会,20分其实考了18.5。A还问她考试的时候为啥老师站在她边上看了好久。说实话老师真记不起来了。
转自宋基会嘉公益 原文: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vWU_0nFypzUanO_IkT4wzQ (音频版) 作者:赵淑萍、南昭瑾
我国的青藏高原广泛发育有冰川、冻土、沼泽、湖泊等地貌。冰川素有“天然固态水库”之称,青藏高原冰川储量约占亚洲冰储量的三分之一,中国整体冰储量的80%多,是地球上除南北极外冰储量最大的地方,被誉为“地球第三极”。青藏高原还有广泛的多年冻土分布,在土里储藏着大量的地下冰,据一个初步研究,地下冰储量是青藏高原地下水储量的10倍、是冰川储量的2-3倍。青藏高原上分布的湖泊占了中国湖泊数量与面积的一半,储藏着大量水资源。青藏高原被誉为“世界屋脊”,平均海拔4000米以上,就像一座天然的高塔,将冰雪融水源源不断的向外输送,孕育了黄河、长江、澜沧江、怒江、雅鲁藏布江等多条亚洲重要河流,向亚洲近20亿人供应着淡水。所以,这也是青藏高原被称为“亚洲水塔”的原因。
Continue reading赵奕,南卓铜*,李祥飞,徐毅,张凌. 分布式水文模型DHSVM在西北高寒山区流域的适用性研究. 冰川冻土. 2019, 41(1): 147-157.
分布式水文-土壤-植被模型(Distributed Hydrology Soil Vegetation Model, DHSVM)是基于栅格离散的分布式水文模型,对地表水热循环的各个过程能进行很精细地刻画,被广泛应用于世界各地很多类型的流域的高时空分辨率的水文模拟,然而它在高寒山区的适用性并不清楚。基于300m数字高程模型,应用DHSVM 模型对典型的高寒山区流域八宝河流域2001-2009年的水文过程展开模拟,并采用流域出口祁连站的水文实测数据对模型进行了精度评价。参数敏感性分析表明,土壤横向导水率、田间持水量和植被反照率等是该区域主要的敏感性参数。模型默认参数会高估高寒山区流域的潜在蒸散发量,导致夏季径流量远小于观测值。通过参数率定,模型校准期(2001-2004)的模拟日径流和月径流Nash 效率系数分别达到0.72 和0.87;而模型验证期(2005-2009)分别为0.60 和0.74 。结果表明,DHSVM 模型基本具备了模拟高寒山区流域降水-径流过程的能力。然而,由于DHSVM 模型缺少对高寒山区流域土壤的冻融过程的刻画,春季径流的模拟精度明显受到影响,需要在将来重点改进。
下载 (pdf, ~1.86 MB):
期刊官网:Link
Cao Y, Nan Z, Cheng G, Zhang L. Hydrological variability in the arid lands of northwest China during 2002-2013. Advances in Meteorology. 2018, 2018(1502472): 1-13. DOI:10.1155/2018/1502472.
Abstract:
The arid region of Northwest China (ANC) has a distinct and fragile inland water cycle. This study examined the hydrological variations in ANC and its three subregions from August 2002 to December 2013 by integrating terrestrial water storage (TWS) anomaly data derived from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite, soil moisture data modeled by the Global Land Data Assimilation System, and passive microwave snow water equivalent data. The results show that the TWS in ANC increased at a rate of 1.7mm/a over the past decade, which consisted of an increasing trend of precipitation (0.12mm/a). Spatially, in the northern ANC, TWS exhibited a significant decreasing trend of −3.64 mm/a ( < 0.05) as a result of reduced rainfall, increased glacial meltwater draining away from the mountains, and intensified human activities. The TWS in southern and eastern ANC increased at a rate of 2.14 ( = 0.10) and 1.63 ( < 0.01)mm/a, respectively. In addition to increasing precipitation and temperature, decreasing potential evapotranspiration in Southern Xinjiang and expanding human activities in Hexi-Alashan together led to an overall increase in TWS. Increased glacier meltwater and permafrost degradation in response to climate warming may also affect the regional TWS balance. The variations in soil moisture, groundwater, and surface water accounted for the majority of the TWS anomalies in southern and easternANC.The proposed remote sensing approach combiningmultiple data sources proved applicable and useful to understand the spatiotemporal characteristics of hydrological variability in a large area of arid land without the need for field observations.
原书作者Hipel和McLeod在他们主页上提供公开下载,原网页是 http://www.stats.uwo.ca/faculty/aim/1994Book/。免费使用的条件是:
“We give our permission to use this material freely for teaching provided that the following citation is included: “Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems” by Keith W. Hipel and A. Ian McLeod.”
(我们许可免费使用本书用于教学目的,只要将下述引用包括进来:“Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems” by Keith W. Hipel and A. Ian McLeod.”)
这本关于水文数据时间序列的书长达1千多页,内容十分丰富;遗憾的原网页在国内一些地方被屏蔽,无法访问, 转帖到这里方便国内学者使用。务请尊重原作者许可的使用条件。
Hipel K W, Mcleod A I. Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elesevier, 1994, 1013.
Links: Link1 (Baidu, ~63MB)
Zhang L, Nan Z*, Liang X*, Xu Y, Hernandez F, Li L. Application of the MacCormack Scheme to Overland Flow Routing for High-spatial Resolution Distributed Hydrological Model. Journal of Hydrology. 2018, 558: 421-431.
Abstract:
Although process-based distributed hydrological models (PDHMs) are evolving rapidly over the last few decades, their extensive applications are still challenged by the computational expenses. This study attempted, for the first time, to apply the numerically efficient MacCormack algorithm to overland flow routing in a representative high-spatial resolution PDHM, i.e., distributed hydrology-soil-vegetation model (DHSVM), in order to improve its computational efficiency. The analytical verification indicates that both the semi and full versions of the MacCormack schemes exhibit robust numerical stability and are more computationally efficient than the conventional explicit linear scheme. The full-version outperforms the semi-version in terms of simulation accuracy when a same time step is adopted. The semi-MacCormack scheme was implemented into DHSVM (version 3.1.2) to solve the kinematic wave equations for overland flow routing. The performance and practicality of the enhanced DHSVM-MacCormack model were assessed by performing two groups of modeling experiments in the Mercer Creek watershed, a small urban catchment near Bellevue, Washington. The experiments show that DHSVM-MacCormack can considerably improve the computational efficiency without compromising the simulation accuracy of the original DHSVM model. More specifically, with the same computational environment and model settings, the computational time required by DHSVM-MacCormack can be reduced to several dozen minutes for a simulation period of three months (in contrast with one day and a half by the original DHSVM model) without noticeable sacrifice of the accuracy. The MacCormack scheme proves to be applicable to overland flow routing in DHSVM, which implies that it can be coupled into other PHDMs for watershed routing to either significantly improve their computational efficiency or to make the kinematic wave routing for high resolution modeling computational feasible.
Keywords: MacCormack Scheme; Overland Flow Routing; DHSVM; Kinematic Wave; Computational Efficiency
Links: Link1 (Elesvier, 50day’s free access since Feb 4, 2018) ; Baidu;
Zhang L, Nan Z*, Yu W, Zhao Y, Xu Y. Comparison of baseline period choices for separating climate and land use/land cover change impacts on watershed hydrology using distributed hydrological models. Science of the Total Environment. 2018, 622-623: 1016-1028.
*corresponding author
强德霞,赵彦博,南卓铜*,吴小波. 基于参数实时优化的洪水预报系统研究:以黑河干流洪水为例. 水利水电技术. 2017, 48(4): 13-17.
另:对于里面使用不同模型进行不同场次洪水预报我有不同意见,因为我们无法知道下一场次洪水到底适合何种模型,从而不能实际用起来。但使用实测数据,对给定模型参数进行实时率定,从而优化使用该模型的洪水预报精度,是本文主要想传达的。
Full text available upon request.
推荐一下陈昌春老师汇编的水科学书目,很有用的信息。
水文水资源水科学英文书目概览
南京信息工程大学 陈昌春
该书目概览包含了世界上近50年来大约2500本水文和水科学英语学术著作的简要信息,范围大体包括水文、水资源、水环境、水管理、水经济、水法律等。这本书中介绍的绝大多数学术著作都是正式出版物。此外,收集了大量出版水文和水科学著作的出版机构信息,并特别介绍了一些水科学丛书类著作与大部头、权威性著作。
全文下载地址:
http://prep.istic.ac.cn/preprint/main.html?action=showFile&id=2c928282510e4d7301511dca1a81001e